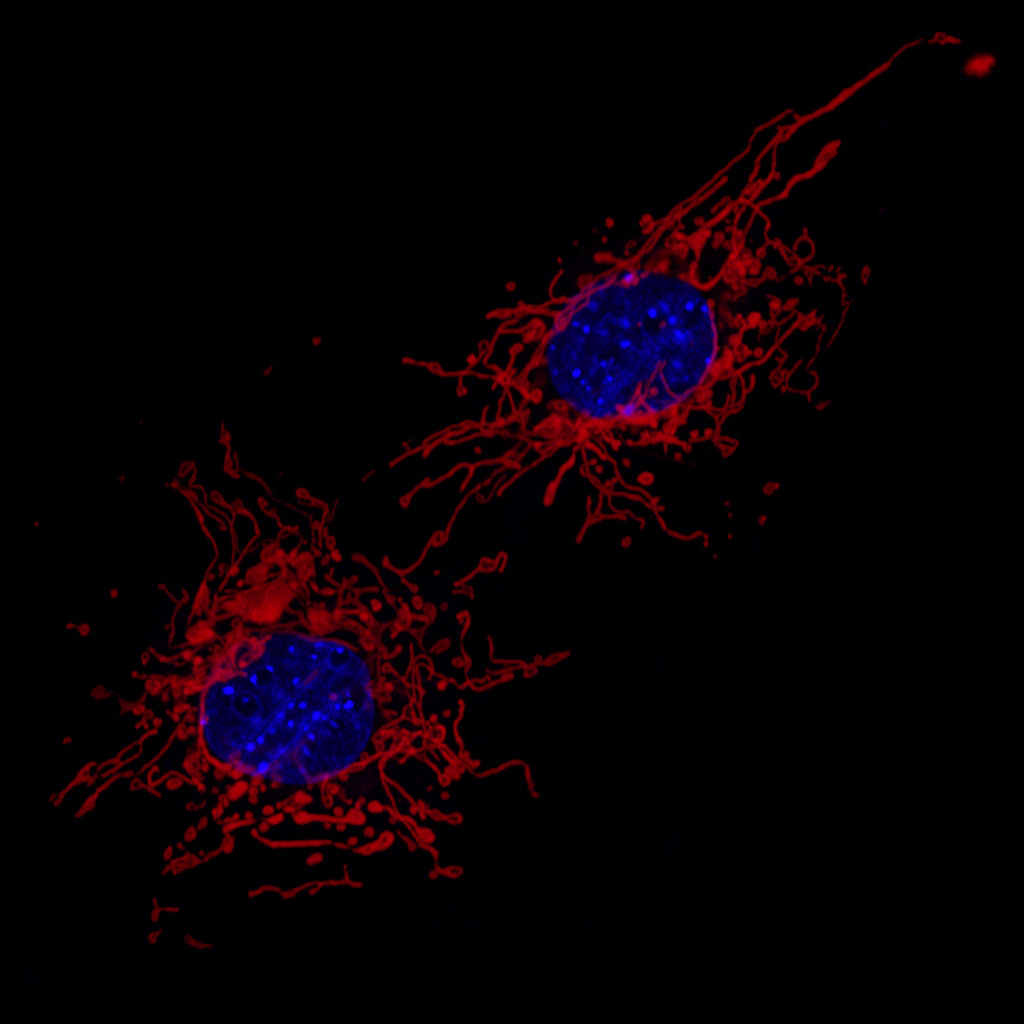
The genus Conus sensu lato consists of 500-700 species. However, the mitochondrial genomes of only few species have been fully sequenced and reported so far.
Structural features of conopeptide genes inferred from partial sequences of the Conus tribblei genome
An impressive biodiversity (>10,000 species) of marine snails (suborder Toxoglossa or superfamily Conoidea) have complex venoms, each containing approximately 100 biologically active, disulfide-rich peptides.

Comparing different post-mortem human samples as DNA sources for downstream genotyping and identification
The capability of DNA laboratories to perform genotyping procedures from post mortem remains, including those that had undergone putrefaction, continues to be a challenge in the Philippines, a country characterized by very humid and warm conditions all year round.
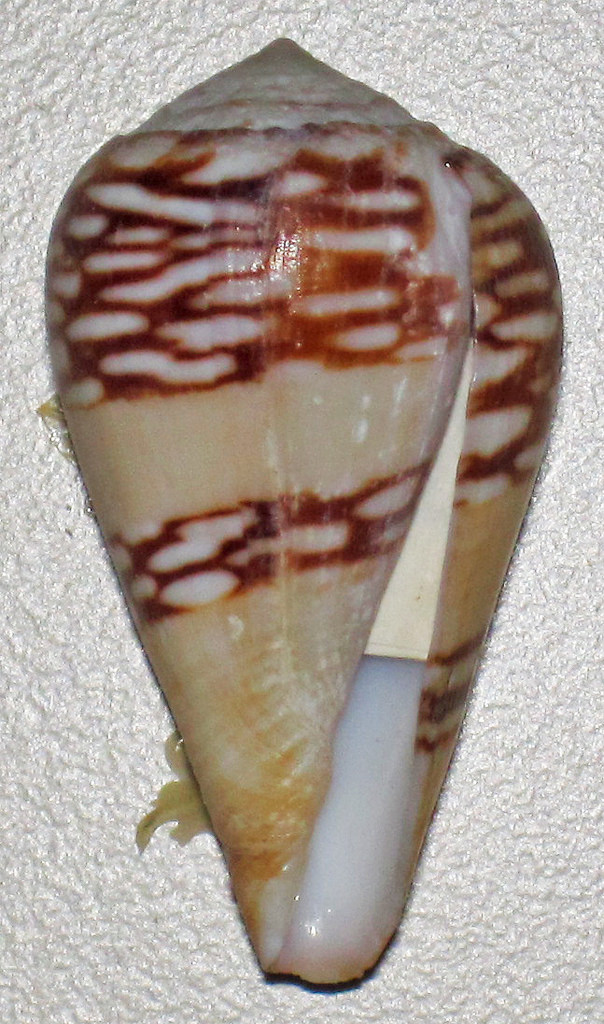

Comparison of the Venom Peptides and Their Expression in Closely Related Conus Species: Insights into Adaptive Post-speciation Evolution of Conus Exogenomes
Genes that encode products with exogenous targets, which comprise an organism’s “exogenome,” typically exhibit high rates of evolution.
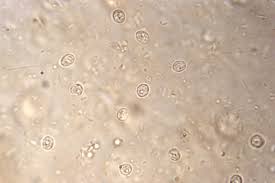
Advancing Cryptosporidium Diagnostics from Bench to Bedside
Cryptosporidium is increasingly being recognized as an important cause of diarrhea worldwide. Although well known for its impact among HIV positive population, improved diagnostic tests have contributed to its emerging recognition one among the most prevalent causes of early childhood moderate to severe diarrhea, persistent diarrhea, and impaired neurocognitive development.
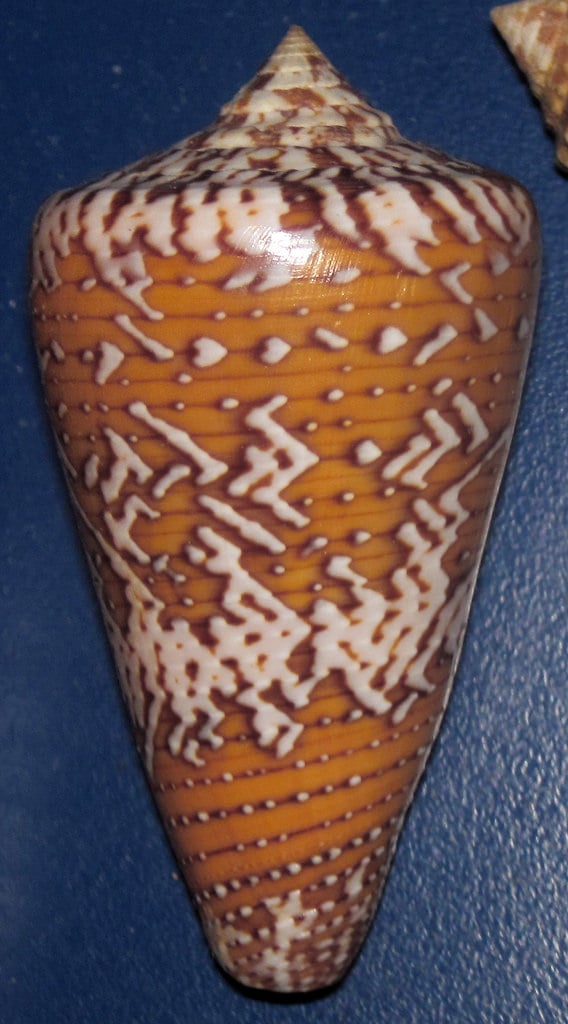

High conopeptide diversity in Conus tribblei revealed through analysis of venom duct transcriptome using two high-throughput sequencing platforms
Barghi N, Concepcion G.P., Olivera B.M., Lluisma A.O.
The venom of each species of Conus contains different kinds of pharmacologically active peptides which are mostly unique to that species.

A bioinformatics survey for conotoxin-like sequences in three turrid snail venom duct transcriptomes
David Thomas T. Gonzales, Cynthia P. Saloma
The repertoire of venom peptides produced by Conoidean snails has shown to be useful for therapeutic and neuropharmacologic applications.
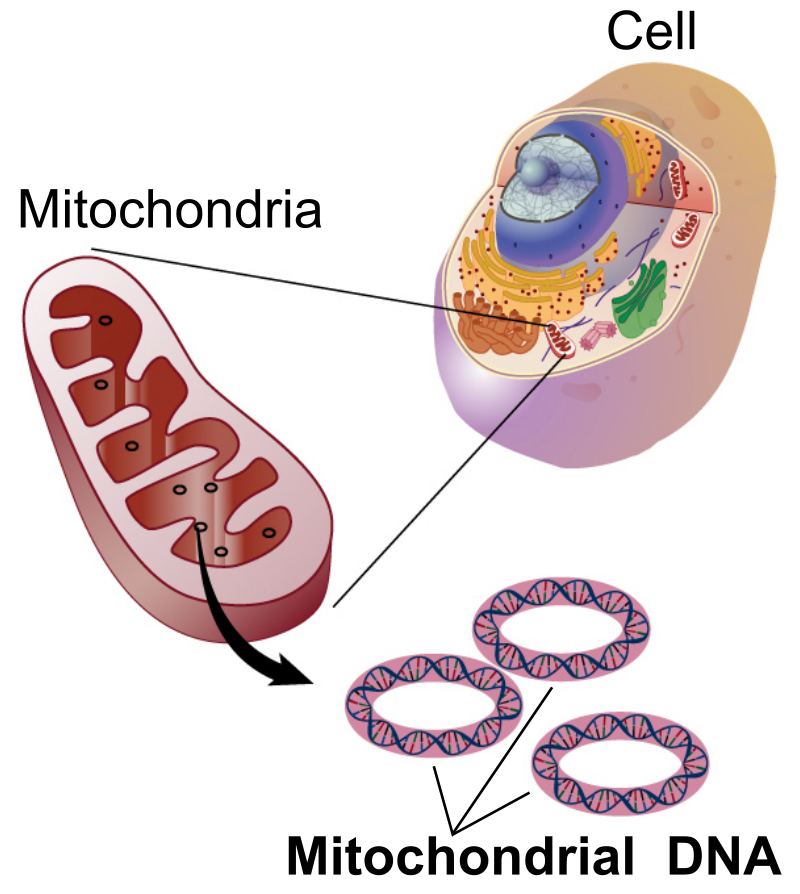
The mitochondrial genome of the red alga Kappaphycus striatus (“Green Sacol” variety): Complete nucleotide sequence, genome structure and organization, and comparative analysis
The complete mitochondrial (mt) DNA sequence of the rhodophyte Kappaphycus striatus (“Green Sacol” variety) was determined.
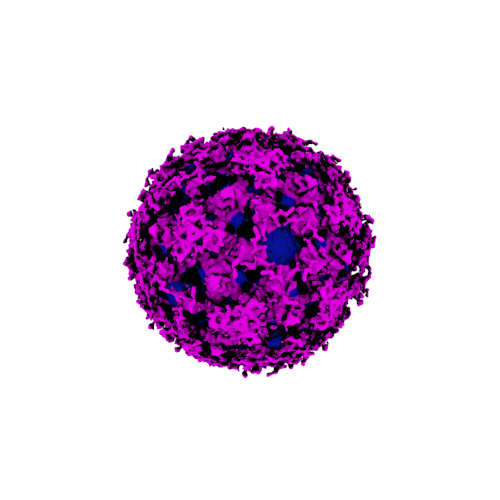
Continued circulation of a single genotype of dengue virus serotype 2 in the Philippines
To obtain descriptive information of behavioral pattern in Chinese school-aged children with cleft lip and palate.
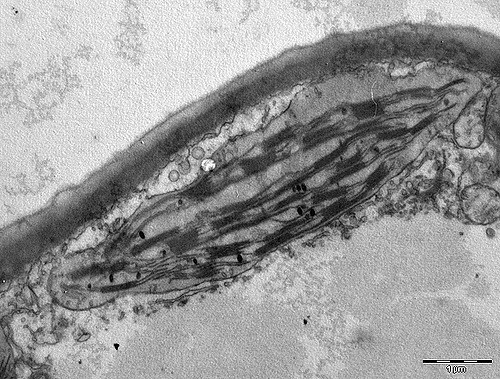
Possible Loss of the Chloroplast Genome in the Parasitic Plant Rafflesia lagascae (Rafflesiaceae)
Rafflesia is a genus of holoparasitic plants endemic to Southeast Asia that has lost the ability to undertake photosynthesis.